How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation, however, requires understanding not only the mechanics of flight but also crucial safety protocols and legal regulations. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly and effectively, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues.
We will explore the fundamental controls, different flight modes, and techniques for capturing stunning aerial footage. Furthermore, we’ll delve into the legal landscape surrounding drone operation, ensuring you comply with all relevant regulations to avoid potential penalties. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to embark on your drone piloting journey with confidence and skill.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both legal regulations and crucial safety procedures. This section covers essential legal requirements in various countries, detailed safety protocols for pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight phases, and a checklist of vital safety equipment.
Drone Laws and Regulations Across Countries
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. Understanding these differences is crucial for legal and safe operation. Failure to comply can lead to fines, confiscation of equipment, or even legal action.
| Country | Licensing Requirements | Flight Restrictions | Penalties for Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for most drones; Part 107 license needed for commercial operation. | Restrictions on flying near airports, people, and sensitive locations; limitations on altitude and flight time. | Fines, loss of drone, potential criminal charges. |
| United Kingdom | Registration is not mandatory for all drones but strongly recommended. Permission may be needed for commercial use. | Restrictions on flying near airports, crowds, and built-up areas; limitations on altitude. | Fines, potential legal action. |
| Canada | Registration is mandatory for most drones. A drone pilot certificate is required for commercial operation. | Similar restrictions to the US and UK, with specific rules regarding privacy and wildlife. | Fines, potential legal action. |
Pre-Flight, In-Flight, and Post-Flight Safety Procedures
A systematic approach to safety is paramount. This involves thorough pre-flight checks, adherence to safe operating practices during flight, and post-flight inspections.
- Pre-flight: Check weather conditions, battery levels, GPS signal, propeller integrity, and surrounding environment for obstacles.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight, avoid obstacles and people, respect airspace restrictions, and monitor battery levels.
- Post-flight: Inspect the drone for damage, secure the drone and its components, and review flight logs.
Essential Safety Equipment Checklist
Having the right equipment can significantly enhance safety and prevent potential incidents.
- Extra batteries
- Spare propellers
- First-aid kit
- Carrying case
- Appropriate clothing for weather conditions
Pre-Flight Checklist and Preparation
A meticulous pre-flight checklist is essential for a safe and successful flight. This section details the steps involved in preparing your drone for flight, including battery management, GPS signal verification, and flight path planning.
Step-by-Step Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Charge the drone battery fully.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and GPS.
- Check the weather conditions.
- Plan the flight path, considering obstacles and airspace restrictions.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Ensure the GPS signal is strong and stable.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration check.
Charging and Calibrating the Drone Battery
Proper battery management is crucial for safe and reliable drone operation. This involves fully charging the battery before each flight and periodically calibrating it to maintain optimal performance and extend its lifespan. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
GPS Signal and Compass Calibration
A strong GPS signal is vital for accurate positioning and autonomous flight modes. Compass calibration ensures the drone correctly orients itself. These steps are usually done via the drone’s app or control interface.
Planning a Safe Flight Path

Careful flight path planning is essential to avoid collisions with obstacles and ensure safe operation. Consider factors such as wind conditions, altitude restrictions, and the presence of buildings, trees, or power lines.
Controlling the Drone: Basic Operations
Understanding the basic controls of a drone is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the basic control inputs, takeoff and landing procedures, and different flight modes.
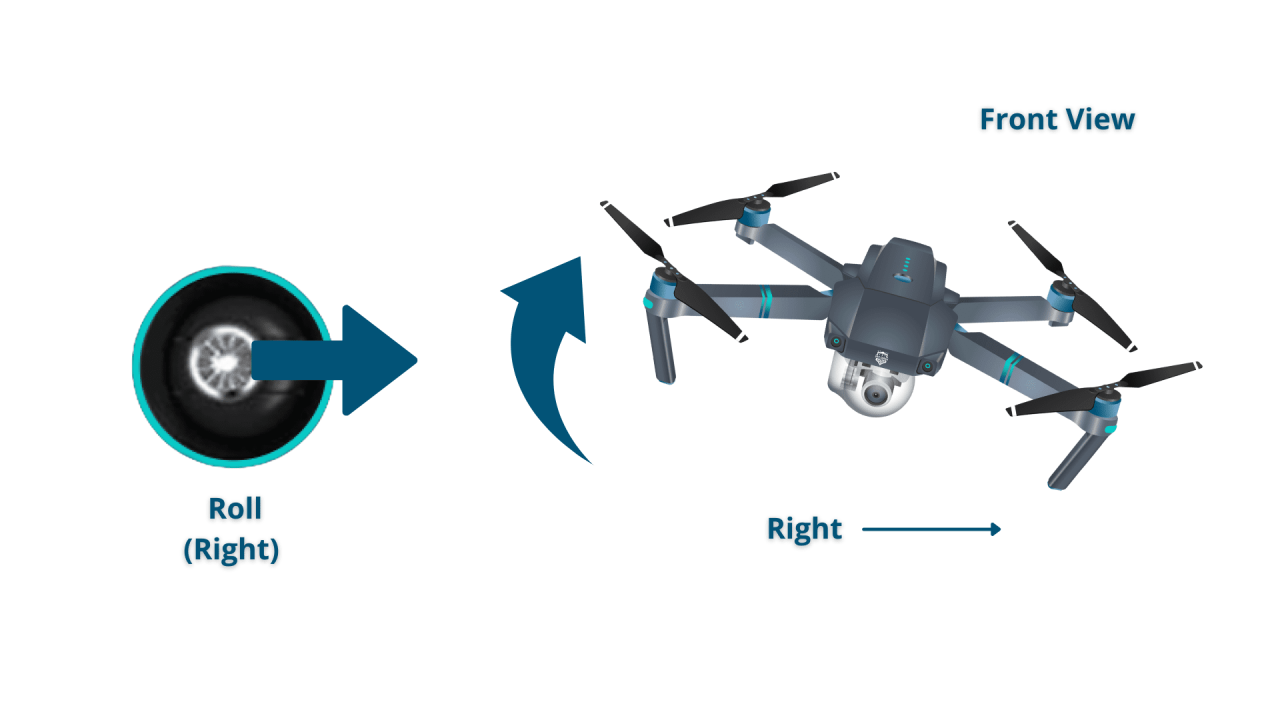
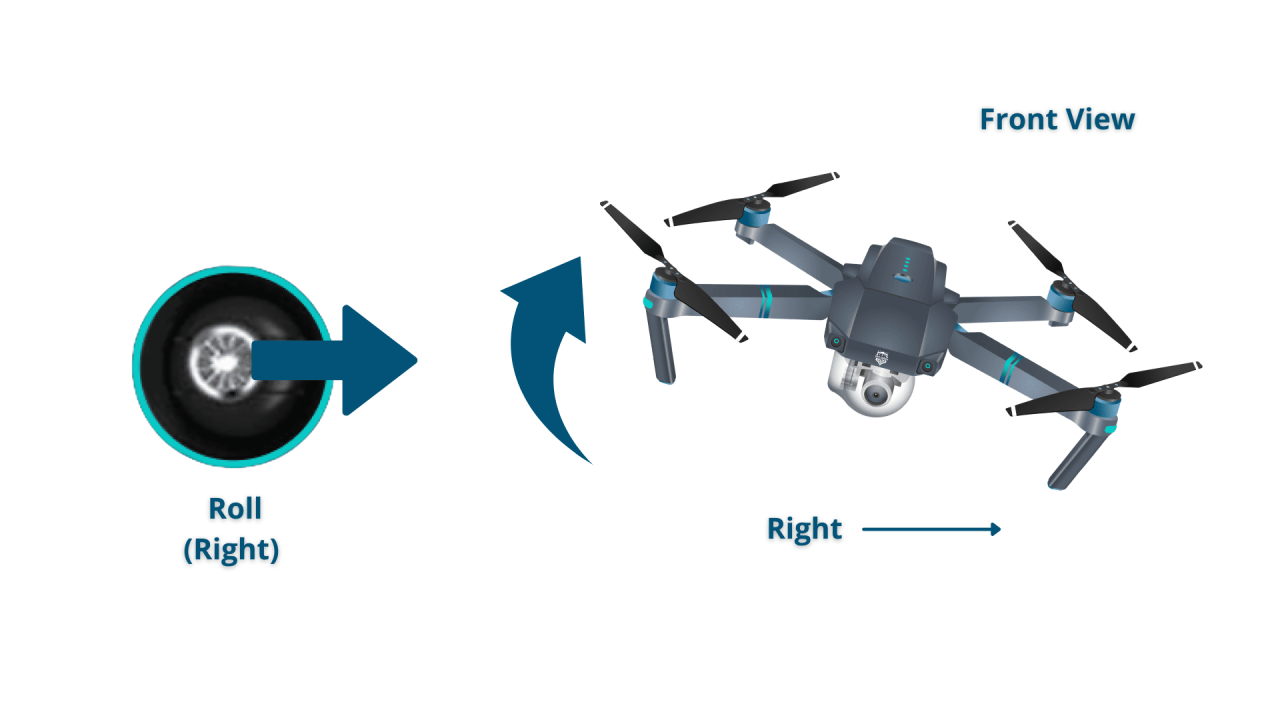
Basic Drone Controls, How to operate a drone
Most drones use four primary controls: throttle (controls altitude), yaw (controls rotation around the vertical axis), pitch (controls forward/backward movement), and roll (controls left/right movement). These are typically controlled via joysticks on the remote controller.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Takeoff and landing should be performed in a clear, open area, away from obstacles and people. A smooth, controlled ascent and descent is crucial. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal requirements, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and responsible flying. Proper training is essential before attempting any flight.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Altitude hold maintains a constant altitude, GPS mode utilizes GPS for position holding, and manual mode provides full control with no stabilization assistance.
Flowchart of a Typical Drone Flight
A visual representation of the steps involved in a typical drone flight can improve understanding and workflow.
A flowchart would visually depict the following steps: Pre-flight checks → Power on → Calibration → Takeoff → Flight maneuvers → Landing → Power off → Post-flight inspection.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Beyond basic flight, drones can perform advanced maneuvers. This section explores these maneuvers, the software used to plan them, and the capabilities of different flight controllers.
Performing Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like circling, orbiting, and waypoint navigation require practice and familiarity with the drone’s controls and flight modes. These maneuvers can enhance the creative possibilities of aerial photography and videography.
Using Drone Software for Complex Flight Plans

Dedicated drone software allows users to plan and execute complex flight paths, including waypoints, orbits, and automated camera movements. This simplifies the creation of professional-looking aerial footage.
Capabilities of Different Drone Flight Controllers
Different drones use various flight controllers, each with its own capabilities and features. Some controllers offer advanced features like obstacle avoidance and autonomous flight modes.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is key, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques. Once you’ve grasped the basics, you’ll be ready to explore the exciting world of drone operation safely and effectively.
Common Drone Maneuvers
- Circling: The drone maintains a circular flight path around a specific point. This is useful for capturing panoramic views or following a subject in motion.
- Orbiting: Similar to circling, but often involves maintaining a constant distance from a subject while rotating around it.
- Waypoints: Pre-programmed points in a flight path that the drone automatically navigates between. This allows for complex, automated flights.
- Follow Me: The drone automatically follows a subject, maintaining a set distance and altitude. Often requires a GPS tracker on the subject.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones are powerful tools for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. This section explores camera settings, techniques for smooth shots, and capturing footage in various lighting conditions.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Understanding camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and white balance is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. These settings affect exposure, depth of field, and overall image appearance.
Achieving Stable and Smooth Shots
Smooth footage is essential for professional-looking results. Techniques such as using a gimbal, flying at a steady pace, and avoiding sudden movements are vital for minimizing vibrations and creating cinematic shots.
Capturing Aerial Footage in Various Lighting Conditions
Lighting conditions significantly impact image quality. Adjusting camera settings and flight strategies are necessary to achieve optimal results in different lighting scenarios, such as bright sunlight, low light, or golden hour.
Comparison of Drone Camera Capabilities
| Drone Model | Camera Resolution | Video Recording Capabilities | Image Stabilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | 20MP | 5.1K video at 50fps | 3-axis gimbal |
| DJI Air 2S | 1-inch sensor, 20MP | 5.4K video at 30fps | 3-axis gimbal |
| Autel Evo II Pro | 48MP | 8K video at 24fps | 3-axis gimbal |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common problems encountered during drone operation and provides troubleshooting steps to resolve them. Regular maintenance is also emphasized.
Common Drone Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully using the manufacturer’s recommended charger. Consider carrying extra batteries.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure a clear view of the sky, away from buildings and obstructions. Try recalibrating the GPS.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motors for damage. If a motor is faulty, it may need replacement.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately. Ensure proper propeller alignment.
- Controller Issues: Check battery levels and connectivity. Try restarting the controller and drone.
Importance of Regular Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and prevents potential problems. This includes cleaning the drone, inspecting components for damage, and lubricating moving parts as needed (according to the manufacturer’s recommendations).
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Proper maintenance and storage are essential for preserving the drone’s functionality and longevity. This section Artikels procedures for cleaning, storage, and regular inspections.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent dirt and debris from affecting the drone’s performance. Use a soft cloth and gentle cleaning solutions as recommended by the manufacturer. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
Safe Storage of the Drone and Accessories
Store the drone and its accessories in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use a protective case to prevent damage during transport and storage.
Regular Inspections for Potential Damage
Regular inspections are vital to identify potential problems early on. Check for loose screws, damaged propellers, or any signs of wear and tear on the drone’s body and components.
Recommended Maintenance Tools and Supplies
- Soft cleaning cloths
- Compressed air
- Screwdrivers (appropriate sizes)
- Protective case
- Spare parts (propellers, etc.)
Operating a drone successfully blends technical skill with a strong understanding of safety and legal requirements. From mastering basic controls to executing advanced maneuvers and capturing professional-quality footage, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the process. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to safety protocols are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the possibilities, but always prioritize safe and legal operation.
FAQs: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and automated return-to-home functions are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and a good safety record.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual mode and carefully guide it back to a safe landing area. Avoid flying in areas with weak GPS reception.
How do I clean my drone’s camera lens?
Use a microfiber cloth and lens cleaning solution specifically designed for camera lenses. Gently wipe the lens in a circular motion, avoiding excessive pressure.
What is the best way to store my drone?
Store your drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Use a protective case to prevent damage during transport and storage.